“Apache Spark Structured Streaming”
Structured Streaming is a stream processing engine built on the Spark SQL engine.
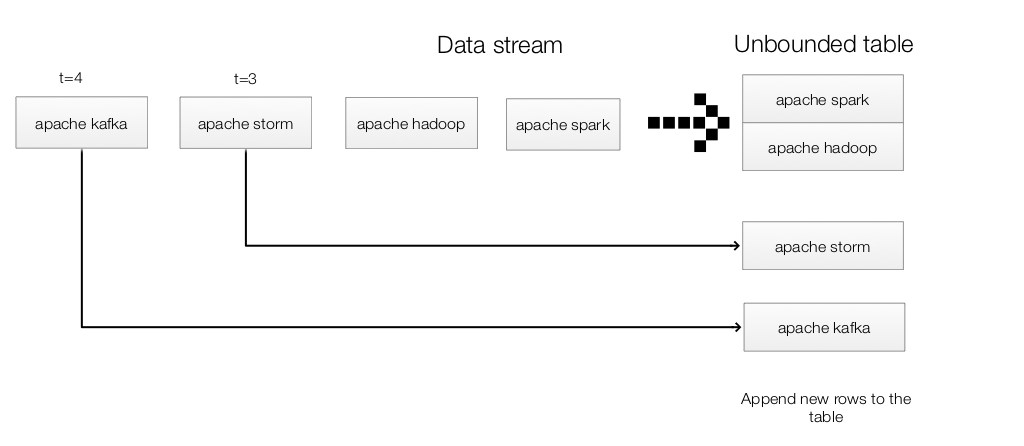
StructuredNetworkWordCount maintains a running word count of text data received from a TCP socket. DataFrame lines represents an unbounded table containing the streaming text. The table contains one column of strings value, and each line in the streaming text data becomes a row in the table.The DataFrame is converted to a Dataset of String using .as[String]. We then apply the flatMap to split each line into words Dataset. Finally, we define the wordCounts DataFrame by grouping it by the word and counting them. wordCounts is a streaming DataFrame representing the running word counts.
package org.apache.spark.examples.sql.streaming
import org.apache.spark.sql.SparkSession
/**
* Counts words in UTF8 encoded, '\n' delimited text received from the network.
*
* Usage: StructuredNetworkWordCount <hostname> <port>
* <hostname> and <port> describe the TCP server that Structured Streaming
* would connect to receive data.
*
* To run this on your local machine, you need to first run a Netcat server
* `$ nc -lk 9999`
* and then run the example
* `$ bin/run-example sql.streaming.StructuredNetworkWordCount
* localhost 9999`
*/
object StructuredNetworkWordCount {
def main(args: Array[String]) {
if (args.length < 2) {
System.err.println("Usage: StructuredNetworkWordCount <hostname> <port>")
System.exit(1)
}
val host = args(0)
val port = args(1).toInt
val spark = SparkSession
.builder
.appName("StructuredNetworkWordCount")
.getOrCreate()
import spark.implicits._
// Create DataFrame representing the stream of input lines from connection to host:port
val lines = spark.readStream
.format("socket")
.option("host", host)
.option("port", port)
.load()
// Split the lines into words
val words = lines.as[String].flatMap(_.split(" "))
// Generate running word count
val wordCounts = words.groupBy("value").count()
// Start running the query that prints the running counts to the console
val query = wordCounts.writeStream
.outputMode("complete")
.format("console")
.start()
query.awaitTermination()
}
}
Finally, we start receiving streaming data and output the running counts to the console.
// Start running the query that prints the running counts to the console
val query = wordCounts.writeStream
.outputMode("complete")
.format("console")
.start()
query.awaitTermination()
The output can be defined in a different mode:
- Complete Mode - The entire Result Table will be written.
- Append Mode - Only new appended rows will be written. (Assume existing rows do not changed.)
- Update Mode - Updated rows in the Result Table will be written.
Sending streams of text to a TCP socket using netcat.
$ nc -lk 9999
apache spark
apache hadoop
$ ./bin/run-example org.apache.spark.examples.sql.streaming.StructuredNetworkWordCount localhost 9999
-------------------------------------------
Batch: 0
-------------------------------------------
+------+-----+
| value|count|
+------+-----+
|apache| 1|
| spark| 1|
+------+-----+
-------------------------------------------
Batch: 1
-------------------------------------------
+------+-----+
| value|count|
+------+-----+
|apache| 2|
| spark| 1|
|hadoop| 1|
+------+-----+
...
Note, query runs on the entire input table. (not just the newly appended rows)

Input sources
Using socket or files in a directory as streaming source:
val spark: SparkSession = ...
// Read text from socket
val socketDF = spark
.readStream
.format("socket")
.option("host", "localhost")
.option("port", 9999)
.load()
socketDF.isStreaming // Returns True for DataFrames that have streaming sources
socketDF.printSchema
// Read all the csv files written atomically in a directory
val userSchema = new StructType().add("name", "string").add("age", "integer")
val csvDF = spark
.readStream
.option("sep", ";")
.schema(userSchema) // Specify schema of the csv files
.csv("/path/to/directory") // Equivalent to format("csv").load("/path/to/directory")
Selection, Projection, Aggregation
case class DeviceData(device: String, deviceType: String, signal: Double, time: DateTime)
val df: DataFrame = ... // streaming DataFrame with IOT device data with schema { device: string, deviceType: string, signal: double, time: string }
val ds: Dataset[DeviceData] = df.as[DeviceData] // streaming Dataset with IOT device data
// Select the devices which have signal more than 10
df.select("device").where("signal > 10") // using untyped APIs
ds.filter(_.signal > 10).map(_.device) // using typed APIs
// Running count of the number of updates for each device type
df.groupBy("deviceType").count() // using untyped API
// Running average signal for each device type
import org.apache.spark.sql.expressions.scalalang.typed
ds.groupByKey(_.deviceType).agg(typed.avg(_.signal)) // using typed API
Windows operation on event time
We want to have a 10-minutes window that report on every 5 minutes:

Source: [https://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/structured-streaming-programming-guide.html]
import spark.implicits._
val words = ... // streaming DataFrame of schema { timestamp: Timestamp, word: String }
// Group the data by window and word and compute the count of each group
val windowedCounts = words.groupBy(
window($"timestamp", "10 minutes", "5 minutes"),
$"word"
).count()
Handling Late Data and Watermarking
Late arrived data can be updated in the correct window:

Source: [https://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/structured-streaming-programming-guide.html]
In the update mode, rows in the result table can be updated. To reduce the amount of intermediate in-memory state to maintain, we keep a watermarking as a threshold on how late a data can arrive.
import spark.implicits._
val words = ... // streaming DataFrame of schema { timestamp: Timestamp, word: String }
// Group the data by window and word and compute the count of each group
val windowedCounts = words
.withWatermark("timestamp", "10 minutes")
.groupBy(
window($"timestamp", "10 minutes", "5 minutes"),
$"word")
.count()
Some sinks (like files) do not supported the updates that the Update Mode required. In Append Mode, new rows will not be appended until the watermarking period has passed so we can account for late arrived data.
Join operations
Static DataFrames can be joined with streaming DataFrame:
val staticDf = spark.read. ...
val streamingDf = spark.readStream. ...
streamingDf.join(staticDf, "type") // inner equi-join with a static DF
streamingDf.join(staticDf, "type", "right_join") // right outer join with a static DF
Streaming Deduplication
To filter duplicate records:
val streamingDf = spark.readStream. ... // columns: guid, eventTime, ...
// Without watermark using guid column
streamingDf.dropDuplicates("guid")
// With watermark using guid and eventTime columns
streamingDf
.withWatermark("eventTime", "10 seconds")
.dropDuplicates("guid", "eventTime")
Output sink
File based
writeStream
.format("parquet") // can be "orc", "json", "csv", etc.
.option("path", "path/to/destination/dir")
.start()
For debugging
// Write to console
writeStream
.format("console")
.start()
// To memory
writeStream
.format("memory")
.queryName("tableName")
.start()
// ========== DF with no aggregations ==========
val noAggDF = deviceDataDf.select("device").where("signal > 10")
// Print new data to console
noAggDF
.writeStream
.format("console")
.start()
// Write new data to Parquet files
noAggDF
.writeStream
.format("parquet")
.option("checkpointLocation", "path/to/checkpoint/dir")
.option("path", "path/to/destination/dir")
.start()
// ========== DF with aggregation ==========
val aggDF = df.groupBy("device").count()
// Print updated aggregations to console
aggDF
.writeStream
.outputMode("complete")
.format("console")
.start()
// Have all the aggregates in an in-memory table
aggDF
.writeStream
.queryName("aggregates") // this query name will be the table name
.outputMode("complete")
.format("memory")
.start()
spark.sql("select * from aggregates").show() // interactively query in-memory table
Managing Streaming Query
val query = df.writeStream.format("console").start() // get the query object
query.id // get the unique identifier of the running query that persists across restarts from checkpoint data
query.runId // get the unique id of this run of the query, which will be generated at every start/restart
query.name // get the name of the auto-generated or user-specified name
query.explain() // print detailed explanations of the query
query.stop() // stop the query
query.awaitTermination() // block until query is terminated, with stop() or with error
query.exception // the exception if the query has been terminated with error
query.recentProgress // an array of the most recent progress updates for this query
query.lastProgress // the most recent progress update of this streaming query
val spark: SparkSession = ...
spark.streams.active // get the list of currently active streaming queries
spark.streams.get(id) // get a query object by its unique id
spark.streams.awaitAnyTermination() // block until any one of them terminates
Monitoring Streaming Queries
Interactive API:
val query: StreamingQuery = ...
println(query.lastProgress)
/* Will print something like the following.
{
"id" : "ce011fdc-8762-4dcb-84eb-a77333e28109",
"runId" : "88e2ff94-ede0-45a8-b687-6316fbef529a",
"name" : "MyQuery",
"timestamp" : "2016-12-14T18:45:24.873Z",
"numInputRows" : 10,
"inputRowsPerSecond" : 120.0,
"processedRowsPerSecond" : 200.0,
"durationMs" : {
"triggerExecution" : 3,
"getOffset" : 2
},
"eventTime" : {
"watermark" : "2016-12-14T18:45:24.873Z"
},
"stateOperators" : [ ],
"sources" : [ {
"description" : "KafkaSource[Subscribe[topic-0]]",
"startOffset" : {
"topic-0" : {
"2" : 0,
"4" : 1,
"1" : 1,
"3" : 1,
"0" : 1
}
},
"endOffset" : {
"topic-0" : {
"2" : 0,
"4" : 115,
"1" : 134,
"3" : 21,
"0" : 534
}
},
"numInputRows" : 10,
"inputRowsPerSecond" : 120.0,
"processedRowsPerSecond" : 200.0
} ],
"sink" : {
"description" : "MemorySink"
}
}
*/
println(query.status)
/* Will print something like the following.
{
"message" : "Waiting for data to arrive",
"isDataAvailable" : false,
"isTriggerActive" : false
}
*/
Asynchronous API
Query listener:
val spark: SparkSession = ...
spark.streams.addListener(new StreamingQueryListener() {
override def onQueryStarted(queryStarted: QueryStartedEvent): Unit = {
println("Query started: " + queryStarted.id)
}
override def onQueryTerminated(queryTerminated: QueryTerminatedEvent): Unit = {
println("Query terminated: " + queryTerminated.id)
}
override def onQueryProgress(queryProgress: QueryProgressEvent): Unit = {
println("Query made progress: " + queryProgress.progress)
}
})
Recovering from Failures with Checkpointing
aggDF
.writeStream
.outputMode("complete")
.option("checkpointLocation", "path/to/HDFS/dir")
.format("memory")
.start()